Life Science
Sub-micron imaging of soft and solid biological samples
- 3D imaging of biological samples in their natural surroundings
- Imaging of plant roots still embedded in their original soil without any special sample preparation
- Imaging of fragile animals and plants without any sample preparation and sectioning
- Sub-micron imaging of solid structures like seeds as a whole
- Cells culture growth
- Biomedical Application: Artificial Bone Graft Analysis
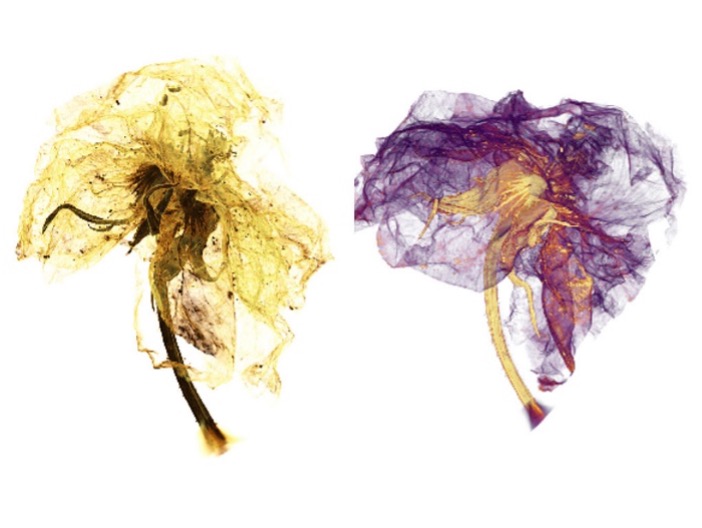
The XRM micrograph of a blossom reveals its components in a new 3D view. Sepals (yellow) and petals (purple) can be distinguished.
(Source: https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/int/products/x-ray-microscopy/zeiss-xradia-610-and-620-versa.html).
Seeds are very solid and compact structures, and their inside is difficult to image as a whole. The image shows the pre-shaped seed leaves which will contain the energy reservoir for the further grow of the plant.
(Source: https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/int/products/x-ray-microscopy/zeiss-xradia-610-and-620-versa.html).
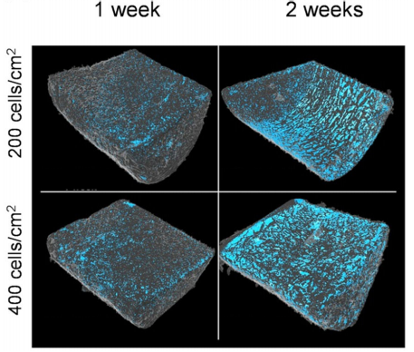
3D reconstructions of PCL scaffolds seeded with two different concentrations of cells, measured after 1 and 2 weeks. The spatial distribution the cells is shown in blue, providing a vision of the cell proliferation trend over time.
(Source: A. Parrilli, S. Pagani and M. C. Maltarello, "Three‐dimensional cellular distribution in polymeric scaffolds for bone regeneration: a microCT analysis compared to SEM, CLSM and DNA content," Journal of Miccroscopy, vol. 255, no. 1, pp. 20-29, 2014).
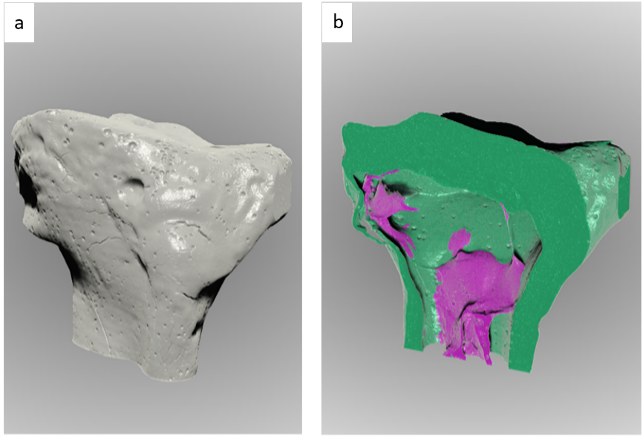
(a) 3D rendering of an Artificial Tibia Bone Graft and (b) the clipped and segmented view. XRM has been used as a powerful tool to investigate the quality of the graft. The trabecular area (purple) is not homogenously porous and dispersed inside the cortical area (green) hence the fabrication process failed.
(Source: F. Cognigni, “Application of Sub-micron 3D X-ray Microscopy in the Artificial Bone Grafting: The Pore Analysis, Master Thesis 2021).



